A Fond Farewell to My Additive Friends
In his final “Additive Insights” column, Tim Simpson reflects on how additive manufacturing has progressed in the last six years. Standards and software are two examples.
Share





All good things must come to an end, as they say, and so it is for my column — but not for additive manufacturing (AM) by any means. If anything, AM is on more solid footing now than it was six years ago when I wrote my first column, and its future looks brighter than ever.
The changes over the last six years have been remarkable. AM systems are , and prices on machines and materials continue to fall. Reliability and repeatability have improved dramatically given all that has been learned about the process physics underpinning the different technologies. We can now model and simulate AM processes to help optimize process parameters faster and reduce the likelihood of build failures, saving companies hundreds of thousands of dollars, if not more, during ramp up to additive production.
Meanwhile, interest in tools and generative design software continues to increase given the ability to optimize and lightweight components with AM. Established software providers are investing in their CAD and CAE tools like never before, and dozens of new startups have emerged to provide new design capabilities and tools, many of which have already been acquired and integrated into existing software to improve the digital workflow that underpins AM.
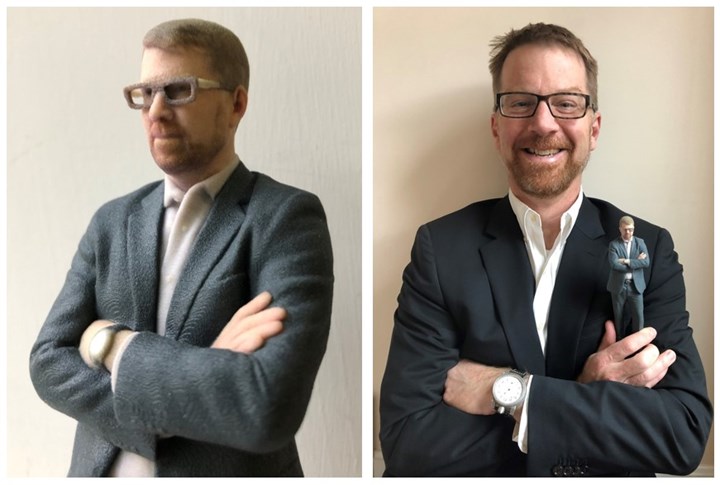

Me and my 3D printed replica from Doob-3D. The 3D printed replica is made from my “digital twin” which was created using full-body 3D imaging technology. Photo Credit: Tim Simpson
While new software tools for design abound, the future is full of potential for AM materials. As our understanding of the process physics has improved, so has our ability to design and tailor alloys, microstructures and properties to different applications. The ability to at once to vary alloy composition and functionally grade an AM component opens up entirely new realms for designers to engineer superior parts and products. The material freedoms of AM have long been overshadowed by the focus on design freedom, but that is certain to change in the near future.
have also advanced rapidly over the past decade, particularly the last few years — an unexpected benefit from the pandemic lockdown. This is great for companies new to AM, but it is easy to get overwhelmed by all of the options that are now available. Thankfully, are pushing another standards coordination effort to identify gaps and ways to harmonize the plethora of standards that have finally been created in response to the demands from industry.
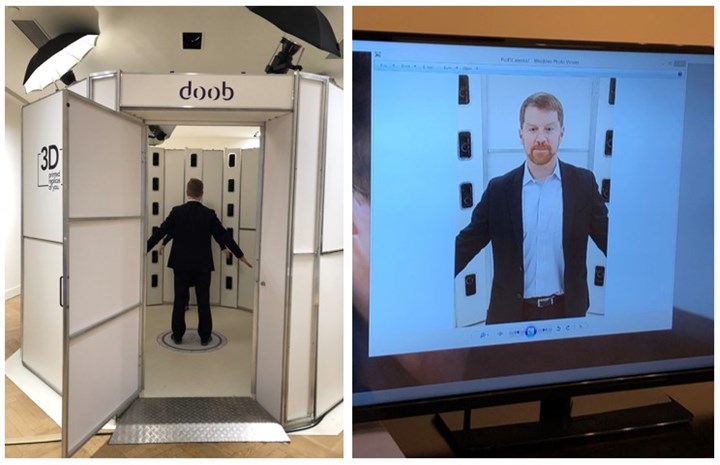

Me getting 3D scanned to create my “digital twin” so that I could be 3D printed.
Photo Credit: Tim Simpson
In addition to new standards, requirement documents for AM parts have been publicly released for aerospace materials systems by and for space flight by . These add to the growing body of regulatory policies and guidance documents that have existed in several fields, including the medical industry which embraced AM early. These not only help boost the confidence for companies new to the game but also strengthen the return on investment that many companies have been anxiously awaiting.
While making a compelling business case for AM may still seem far off for many, companies in nearly every industry have found a way to profit from AM, including metals. Medical implants have been transformed by AM, following suit behind hearing aids, aligners and dental implants. The space industry has fully embraced AM and is pushing the boundaries on performance and productivity faster than most people think possible. Meanwhile, legacy parts for automotive, aerospace and defense applications can now be easily replaced, and many supply chain disruptions can be alleviated with AM. In fact, thanks to the resiliency that AM showed during the pandemic, government programs like are poised to transform the supply chain and help regionalize manufacturing. This is good for the economy and exciting for the workforce, but the fight for talent will only intensify. Companies will need to invest in their people as well as their products and processes; otherwise, the competitive advantage that AM enables will not materialize if the talent is not there to help.
It is clear that the future of manufacturing will be digital, thanks to AM and other advanced manufacturing technologies that rely so heavily on data. The data being generated during the process is already being harnessed to create “digital twins” that will contribute to the “digital thread” that will tie the “digital workflow” and the “digital factory” together. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to assist and will play a critical role in ensuring part quality as companies shift to production with AM and other digital manufacturing technologies.
While this may frighten some of you, I believe the future of manufacturing is brighter than ever before, and I think the machining experts and manufacturing professionals are poised to be the digital pioneers of the future. Will you accept the challenge and take the risk? I hope so!
Thanks all and good luck!
Related Content
Additive/Subtractive Hybrid CNC Machine Tools Continue to Make Gains (Includes Video)
The hybrid machine tool is an idea that continues to advance. Two important developments of recent years expand the possibilities for this platform.
Read MoreMachine Tool Drawbar Made With Additive Manufacturing Saves DMG MORI 90% Lead Time and 67% CO2 Emission
A new production process for the multimetal drawbar replaces an outsourced plating step with directed energy deposition, performing this DED along with roughing, finishing and grinding on a single machine.
Read More6 Trends in Additive Manufacturing Technology
IMTS 2024 features a larger Additive Manufacturing Pavilion than ever before, with veteran suppliers alongside startups and newcomers at the front of the West Building. As you browse these exhibitors, as well as booths found elsewhere at the show, keep an eye out for these trends in AM.
Read MoreThe Cool Parts Showcase Seeks Innovative 3D Printed Parts
Do you solve problems with 3D printing? Enter your 3D printed parts in this contest from The Cool Parts Show.
Read MoreRead Next
AMRs Are Moving Into Manufacturing: 4 Considerations for Implementation
AMRs can provide a flexible, easy-to-use automation platform so long as manufacturers choose a suitable task and prepare their facilities.
Read MoreMachine Shop MBA
Making Chips and 91ÊÓƵÍøÕ¾ÎÛ are teaming up for a new podcast series called Machine Shop MBA—designed to help manufacturers measure their success against the industry’s best. Through the lens of the Top Shops benchmarking program, the series explores the KPIs that set high-performing shops apart, from machine utilization and first-pass yield to employee engagement and revenue per employee.
Read MoreLast Chance! 2025 Top Shops Benchmarking Survey Still Open Through April 30
Don’t miss out! 91ÊÓƵÍøÕ¾ÎÛ's Top Shops Benchmarking Survey is still open — but not for long. This is your last chance to a receive free, customized benchmarking report that includes actionable feedback across several shopfloor and business metrics.
Read More